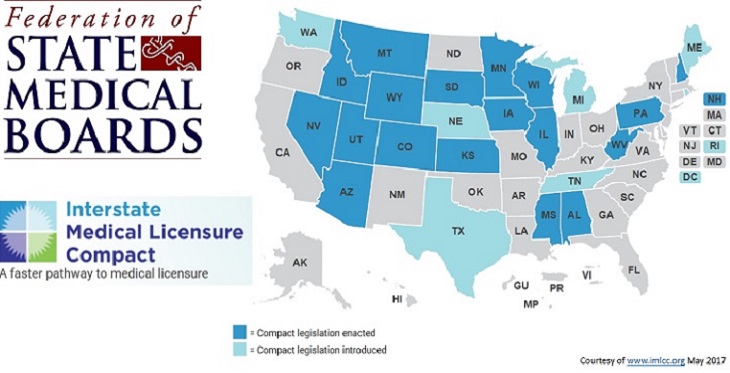
In a watershed moment for the expansion of telemedicine, the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact Commission is now processing applications to allow physicians to practice telemedicine across state lines with greater ease. Nineteen states have passed legislation to adopt the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which allows physicians to obtain a license to practice medicine in any Compact state through a simplified application process. Under the new system, participating state medical boards retain their licensing and disciplinary authority, but agree to share information essential to licensing, creating a streamlined process.
The Federation of State Medical Boards’ President and CEO, Humayun Chaudhry, DO, MACP, called the Compact a “milestone” for medical regulation in the United States. “The launch of the Compact will empower interested and eligible physicians to deliver high-quality care across state lines to reach more patients in rural and underserved communities. This is a major win for patient safety and an achievement that will lessen the burden being felt nationwide as a result of our country’s physician shortage.”
States currently participating in the Compact are Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Nevada, Arizona, Utah, Colorado, South Dakota, Kansas, Minnesota, Iowa, Wisconsin, Illinois, Mississippi, Alabama, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, New Hampshire, and Nebraska. Seven additional states have proposed legislation to adopt the Compact, including Washington, D.C.
Most states require a physician to obtain a license to practice medicine in each state where the patient is located at the time of the physician-patient encounter. Prior to adoption of the Compact, obtaining licensure in a given state was an oppressive task, requiring the physician to complete lengthy applications, submit required documentation, pay fees, and pass examinations. This proved to be a burdensome restriction for physicians practicing telemedicine, where patients may be located in any state at the time of the physician-patient encounter. Licensing requirements were identified as a significant barrier to the expansion of telemedicine, prompting introduction of the Compact.
Physicians are eligible to apply for the Compact license if they possess a full and unrestricted license to practice medicine in a Compact state and have not been disciplined by any state medical board, among other requirements. To apply, the physician must designate a Compact state as the “state of principal licensure” and select the other Compact states in which they would like to become licensed. The state of principal licensure will verify the physician’s eligibility and provide credential information to the Interstate Commission. The Interstate Commission then collects applicable fees and transmits the physician’s information to the additional states, where the licenses will then be granted.
Participation in the Compact creates another pathway for licensure, but does not otherwise change a state’s existing Medical Practice Act. Physicians located in a state that has not adopted the Compact may still obtain licensure in other states through the ordinary licensure process.